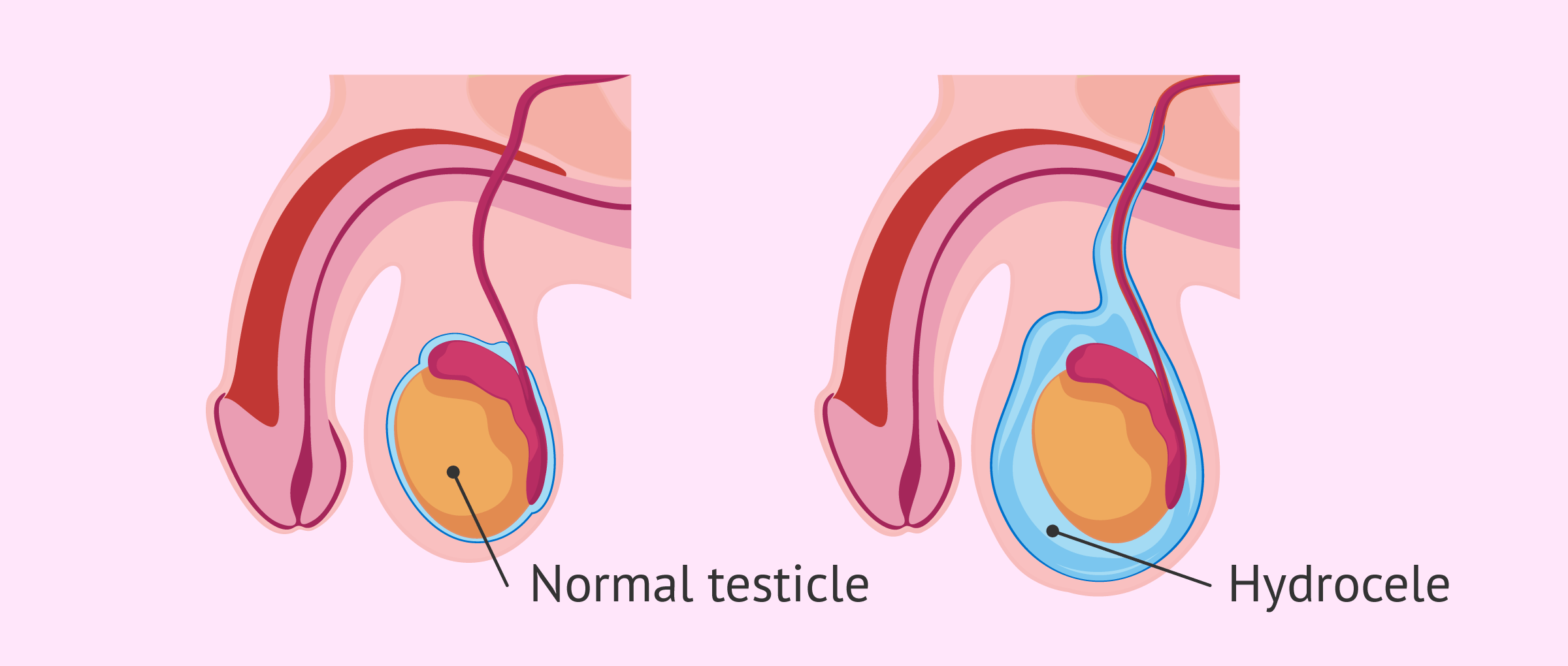
A hydrocele is when fluid fills a male’s scrotum, causing it to swell. It is not a major health issue but it can be embarrassing and uncomfortable. Hydroceles are more common in male infants than adults, and there are treatments to solve the problem. In baby boys, a hydrocele sometimes disappears on its own. But for males of any age, it’s important for a doctor to evaluate a hydrocele because it can be associated with an underlying testicular condition.
A hydrocele that doesn’t disappear on its own might need to be surgically removed, typically as an outpatient procedure. The surgery to remove a hydrocele (hydrocelectomy) can be done under general or regional anesthesia. An incision is made in the scrotum or lower abdomen to remove the hydrocele. If a hydrocele is found during surgery to repair an inguinal hernia, the surgeon might remove the hydrocele even if it’s causing no discomfort.
After hydrocelectomy, you might need a tube to drain fluid and a bulky dressing for a few days. Your doctor is likely to recommend a follow-up exam because a hydrocele might recur.
There are two: communicating hydrocele and non-communicating hydrocele.
A healthcare provider can diagnose a hydrocele in a child or adult through a combination of tests and observations, including:
There are no medications available to treat a hydrocele.
A hydrocele usually does not need to be surgically repaired. A hydrocele typically goes away on its own within six to 12 months of age. If the hydrocele does not resolve on its own, then it needs to be surgically repaired to prevent further complications.

Copyright © 2025 Dr. Sandhya Bade | All Rights Reserved | Created & Crafted By Itorix Infotech
WhatsApp us
